The nutritional value of pulses per 100 grams provides a well-rounded profile of macronutrients and micronutrients. It contains a lot of protein, fiber, and important vitamins and minerals like iron, potassium, and folate. These nutrients play vital roles in maintaining overall health, from boosting the immune system to improving digestion. And we will briefly discuss the nutritional value of pulses per 100gm in this blog.
Pulses, a group of legumes that includes beans, lentils, peas, and chickpeas, are a staple food in many cultures worldwide. Legumes are versatile in cooking and have great nutritional value. This article looks at the calories in legumes, their health benefits, and why they are important for a healthy diet. (1)
Calories in Pulses

Pulses have about 300-400 calories per 100 grams when dried, but this amount decreases when cooked because they absorb water. The calorie content can vary slightly depending on the type of pulse. For instance, cooked pulses like lentils and beans usually have around 100-150 calories per 100 grams. These calories come from a combination of complex carbohydrates, protein, and a small amount of fat.
Nutritional value of pulses per 100g
Pulses are not only low in calories but also packed with essential nutrients. They are a rich source of complex carbohydrates, protein, dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Pulses are nutritious and are a great option for anyone wanting to eat more plant-based foods in their diet.
Protein in Pulses per 100g
Protein is one of the standout nutrients in pulses. On average, pulses provide about 20-25 grams of protein per 100 grams when dried. They are a great plant-based protein source, essential for muscle recovery, growth, and overall body functions.
Protein Pulses Chart
Here’s a quick look at the protein content in some common pulses per 100 grams (dried):
– Lentils: 24 grams
– Chickpeas: 19 grams
– Black Beans: 21 grams
– Red Kidney Beans: 23 grams
– Dry Beans (various types): 20-25 grams
Pulses Nutritional Value Chart
Below is a nutritional value chart for pulses per 100 grams (dried):
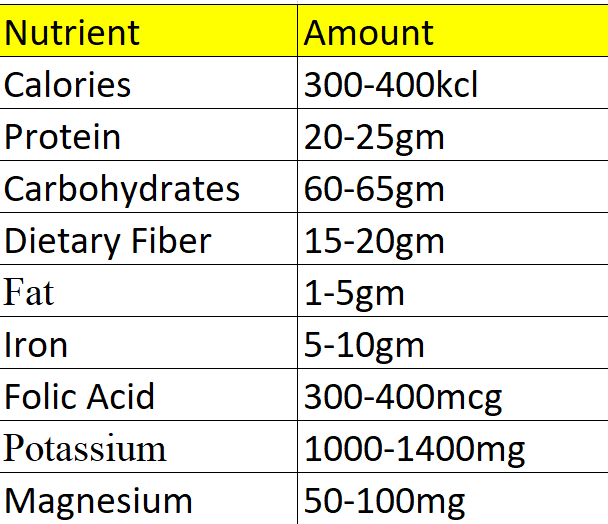
Pulse Calories per 100g
As mentioned, the calorie content of pulses per 100 grams when cooked typically ranges between 100-150 kcal. Pulses are low in calories and can enhance dishes without adding much.
Pulses Nutritional Information
Pulses are packed with nutritional benefits that contribute to overall health and well-being. Here are some key points about pulses’ nutritional information:
– Source of Protein: Pulses are an excellent source of plant-based protein, which is vital for vegetarians and vegans.
– Vitamins and Minerals: Pulses are rich in vitamins and minerals, including B vitamins, folic acid, iron, magnesium, and potassium.
Pulses have complex carbohydrates that give long-lasting energy and do not quickly raise blood sugar levels.
– Low Glycemic Index: Pulses have a low glycemic index, meaning they digest slowly and help regulate blood sugar levels.
100 gm Pulse Protein

If you’re watching your protein intake, 100 grams of pulses give you a lot of protein, similar to animal-based sources. This makes pulses an excellent choice for those looking to increase their protein intake without relying on meat.
Vitamins and Minerals in Pulses
Pulses are rich in several essential vitamins and minerals. Folic acid, for example, is crucial for DNA synthesis and cell division, making it especially important for pregnant women. Iron in pulses helps prevent anemia, while magnesium and potassium contribute to heart health by regulating blood pressure.
Essential Amino Acids in Pulses
While pulses are high in protein, they do not contain all the essential amino acids needed by the body. Pulses, like beans and lentils, are important for a balanced diet when eaten with grains. They provide all essential amino acids.
Glycemic Index of Pulses
Pulses have a low glycemic index (GI). This means they cause a slower and steadier rise in blood sugar levels. This is different from other foods that are high in carbohydrates. This makes pulses an ideal food for people with diabetes or those trying to manage their blood sugar levels.
Health Benefits of Pulses
Reduce the Risk of Chronic Diseases
Eating pulses regularly can reduce the risk of long-term diseases. These diseases include heart disease, diabetes, and some types of cancer. This is due to their high content of dietary fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Reduce Blood Cholesterol
Consuming pulses can reduce blood cholesterol levels, particularly the harmful LDL cholesterol. This could result in a decreased likelihood of developing heart disease and stroke.
Blood Sugar Levels and Blood Pressure
Pulses have a low glycemic index and are high in potassium, which helps control blood sugar and blood pressure. This can improve heart health and lower the risk of heart disease.
Pulses in Food Processing
Pulses are increasingly being used in food processing to create nutritious and functional food products. Pulses are important ingredients in many foods, such as flour and protein sources.
Conclusion
So, the nutritional value of pulses per 100g for peak health regularly incorporate legumes such as chickpeas, peas, lentils, and beans into your diet. They have lots of protein, vitamins, and minerals, and can help prevent diseases. Adding pulses to soups, salads, or stews is a tasty and nutritious way to stay healthy.
If you are interested to read more about food then click here.


1 thought on “Nutritional value of pulses per 100g”